
- #MEASURING STATIC VS STAGNATION PRESSURE USING A PITOT TUBE HOW TO#
- #MEASURING STATIC VS STAGNATION PRESSURE USING A PITOT TUBE FULL#
- #MEASURING STATIC VS STAGNATION PRESSURE USING A PITOT TUBE FREE#
In fact, you can even employ a pitot tube to your project that requires measurement of the velocity of a flow.
It is popular that the instrument is used in aviation, they are also common in industrial machinery, boats, and even sports cars. Pitot tubes can now be found in many applications not only in aviation. Read more: Different types of gas welding processes and its applications Applications of a pitot tube
#MEASURING STATIC VS STAGNATION PRESSURE USING A PITOT TUBE FULL#
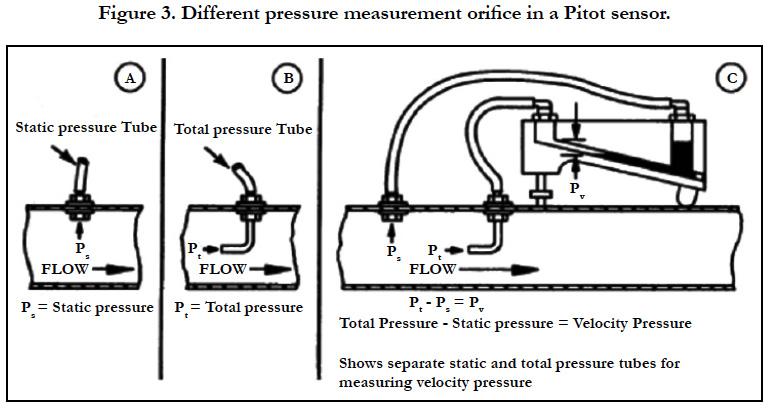
The difference between these two devices is that orifice measures the full flow stream, while the pitot tube can detect the flow velocity at only one point of the flow stream. Also, its flow rangeability of 3:1 (although some work at 4:1) is more like the capacity of the orifice plate. Its accuracy ranges from 0.5% to 5% FS, which is similar to that of an orifice. Pitot tubes which are flow sensor instruments can be an inexpensive alternative to an orifice plate. Measurement between these two pressures is what gives us dynamic pressure, which can be used to calculate airspeed. the side hole measures what’s called static pressure. The front hole is placed in the airstream, helping to measure what is known as stagnation pressure. A pitot tube is a slender tube, having two holes on it. The device was modified to its modern form in the mid-19 th century by a French scientist Henry Darcy. It was invented by Henri Pitot who was a French engineer in the 18 th century. 9 Advantages and disadvantages of a pitot tubeĪ pitot tube is a flow measurement instrument for measuring the velocity (speed) of a flowing fluid.
#MEASURING STATIC VS STAGNATION PRESSURE USING A PITOT TUBE HOW TO#

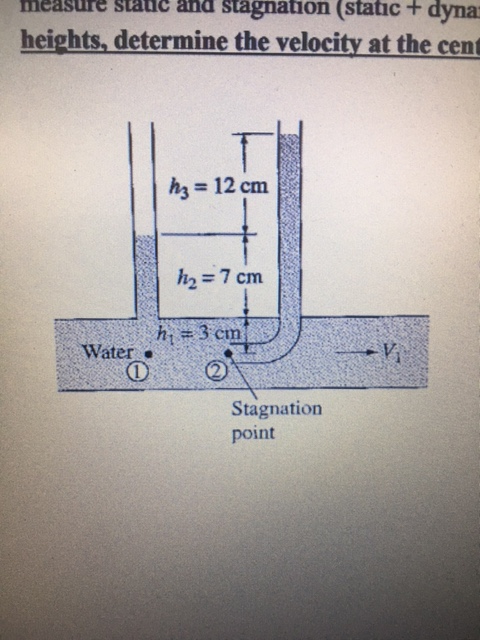
Writing Bernoulli's equation along the stagnation streamline (with Δ z = 0) yields (4) Frictionless deceleration along stagnation streamline. Governing equation: ρ p + 2 V 2 + g z = constant The flowing fluid is air and the manometer liquid is mercury. If the pressure difference is 3 0 mm of mercury, determine the flow speed.Ī Pitot tube inserted in a flow as shown. The static pressure is measured at the same location in the flow, using a wall pressure tap. The tube is inserted so that it points upstream into the flow and the pressure sensed by the tube is the stagnation pressure. The ends of the Pitot tube, measuring the stagnation pressure, and the piezometric tube, measuring the static pressure, may be connected to a suitable differential manometer for the determination of flow velocity and hence the flow rate.Įxample: A Pitot tube is inserted in an air flow (at STP) to measure the flow speed.
A Pitot tube is also inserted as shown (Fig. This is done to sense the static pressure only without any part of the dynamic pressure.
#MEASURING STATIC VS STAGNATION PRESSURE USING A PITOT TUBE FREE#
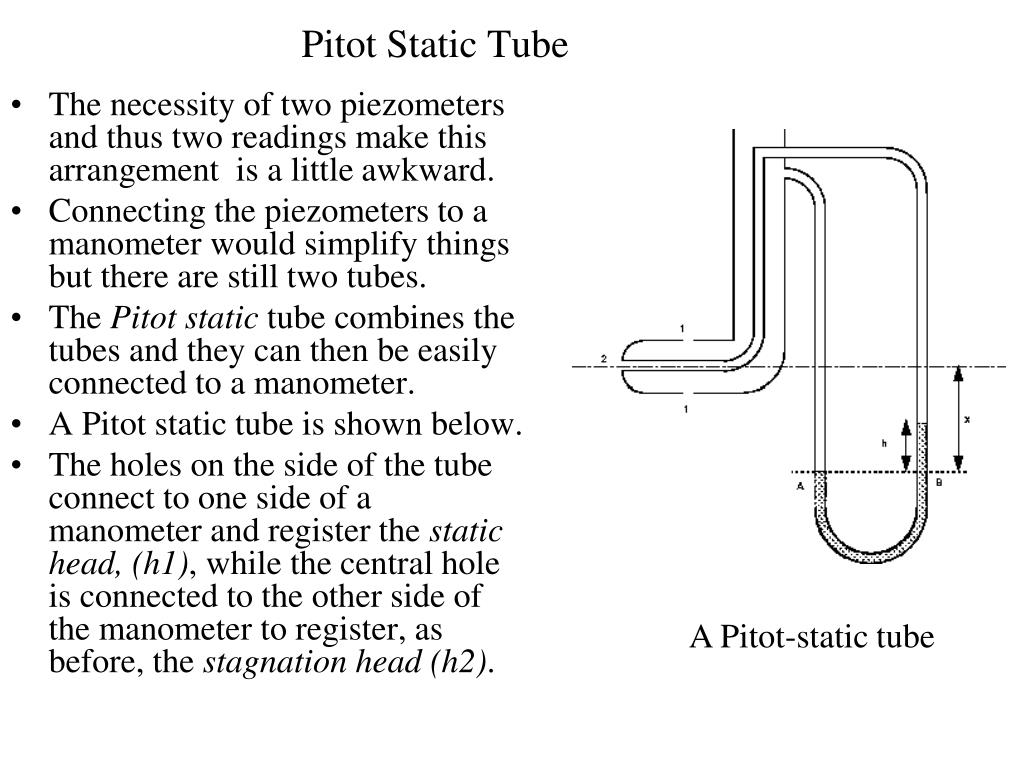
The axis of the tube measuring the static pressure must be perpendicular to the boundary and free from burrs, so that the boundary is smooth and hence the streamlines adjacent to it are not curved. Measurement of static pressure in this case is made at the boundary of the wall (Fig. But for a fluid flowing through a closed duct, the Pitot tube measures only the stagnation pressure and so the static pressure must be measured separately. For an open stream of liquid with a free surface, this single tube is sufficient to determine the velocity. Such a tube is known as a Pitot tube and provides one of the most accurate means of measuring the fluid velocity. Where p 0 , p and V are the stagnation pressure, static pressure and velocity respectively at point A(fig. Therefore, we can write, neglecting friction, Since the static pressure, under this situation, is equal to the hydrostatic pressure due to its depth below the free surface, the difference in level between the liquid in the glass tube and the free surface becomes the measure of dynamic pressure. The liquid flows up the tube and when equilibrium is attained, the liquid reaches a height above the free surface of the water stream. A pitot tube is an open-ended right-angled tube pointing in opposition to the flow of a fluid and used to measure pressure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
